Dear Cyber Professional and Team Member:
October and November 2025 marked another critical and active period in the vulnerability landscape, with over 3,700 new CVEs published and 5,200 modified entries as critical flaws surged across software, hardware, and cloud platforms. US ProTech tracked 31,550 vulnerabilities year-to-date, expanded a correlated threat database containing 1,130 new CVSS v4 and EPSS v4 scores vulnerabilities, and recorded over 2.58 million vendor patch advisories. Exploitation risk remained high, with 408 critical CVEs (of which 13 rated 10) spanning Redis, Flowise, Cisco Firewalls, Microsoft Windows, and WordPress plugins. Cloud-based SSRF and RCE vulnerabilities underscored growing multi-platform attack surface patterns, while WordPress plugin exploits highlighted ongoing supply-chain exposure. Top weaknesses were dominated by code injection (CWE-74), buffer overflows (CWE-119), and SQL injection (CWE-89), confirming attackers’ focus on input-validation and memory-handling flaws.
US ProTech on Fall Vulnerability Trends
Cybersecurity threats continued to burden security professionals, vulnerability analysts and incident responders with specific patterns of exploitable, impactful vulnerabilities and a flurry of increased severities, and widespread across hardware, software, and cloud. The month saw a significant spike accounting of published vulnerabilities to about 3703 during the month, as compared to 3,738 in September and 3,360 in August. This Fall presented the most active month in the vulnerability landscape with a large portion of CVEs updated with newer risk score updates and advisories. US ProTech correlated and archived 31,550 published vulnerabilities so far during the year 2025, well on track to be one of the highest recorded in recent years. The number of modified vulnerabilities accounted for about 5,234 in October alone compared to 5,010 in September and 4,350 with modified risks, priorities, advisories during the month of August. A record 820 vulnerabilities published in August 2025 were revised in September. During the prior 2024 year, October only saw about 3,076 modified CVEs had their risk scores, advisories, and priorities revised, making the current month one of the most active seasons.
US ProTech vendor patch advisories exceeded 2.58M, led by sources including Suse, Ubuntu, Debian, Oracle, and Windows, accounting for nearly 76% of patched advisories issued during the month. US ProTech has consolidated and kept track of nearly 792K affected just in the last 5 years, one of the significant counts.
US ProTech vulnerability data feeds have continued to embrace NVD 2.0 schema for correlating and maintaining our threat intel feeds. Our feed database continues to build upon CVSS4 and EPSS4 risk scoring metrics as part of our threat intel feed, and so far we recorded 9,785 risk scores in 2025 alone, the largest we have seen so far in any year. The first half of Fall accounted for about 1,130 CVSS4 scores aggregated. Specifically, about 71 of those are determined to be critical vulnerabilities of which 23 also have a “higher exploitability percentiles” greater than 60%. A higher EPSS percentile score indicates the likelihood of being exploited in the wild soon in the coming months compared to other similar vulnerabilities in the platform.
Vulnerability Landscape
US ProTech has kept track of nearly 88K exploits so far with exploits, github, metasploit, and packetstorm accounting for a large portion of identified counts.
The number of critical vulnerabilities identified by US ProTech – those with a critical score of 9.0 or higher continued to rise significantly to 408 in October compared to 454 in the previous month. Among those critical vulnerabilities, about 43 of them (~ 10%) had a high likelihood of exploitations in the next few months with a probability of more than 50%.
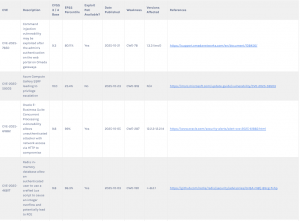
Among those, 13 critical ones (~ 3%) had a perfect 10.0 score observed in several hardware and software drivers and components. Particularly, an SQL Injection vulnerability in Esri ArcGIS Server (CVE-2025-57870) identified across Windows, Linux, and Kubernetes platforms causing unauthenticated users to execute arbitrary SQL commands via specific feature operation; embedded web server missing authentication enabling remote attackers to access and modify device configurations with ABB ALS-mini-S4 and ALS-mini-S8 IP load controllers (CVE-2025-9574); unrestricted IP address vulnerability in ProductivityService PLC Simulator allowing attackers to access or manipulate simulation parameters from any device on the network (CVE-2025-61934).
On the cloud front, Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) vulnerability affects Microsoft Azure Compute Gallery (CVE-2025-59503) where an authorized attacker could exploit this flaw to elevate privileges over a network. The current exploitation risk is high (about 25%), requiring minimal attack and network complexity and only basic privileges, making it easier for attackers to leverage.
Platform Impacts
In October, a series of critical exploitable vulnerabilities affected platforms such as Redis, MLflow, WordPress, Flowise, and Windows, and WordPress plugins with attackers actively targeting these systems for remote code execution, command injection and privilege escalation.
A series of WordPress plugin-based ecosystems are being targeted this Fall, underscoring a need for better plugin validation patch management. Specifically, plugins related to supply chain and open-source business platforms saw increased targeting, as attackers favored platforms with broader deployments for initial access and lateral movement attacks.
A particular Redis in-memory open source vulnerability (CVE-2025-46817) allowed authenticated users to send crafted scripts corrupted memory and the stack, potentially leading to RCE. Redis developers are urged to immediately upgrade or block Lua script execution for untrusted accounts.
Flowise, an open-source low-code user interface platform for building customized large language model workflows, was hit by multiple critical remote code execution vulnerabilities related to insecure dependency handling and flaws in its plugin architecture. Two notable ones in October, CVE-2025-34267 and CVE-2025-61913, stemmed from improper validation of JavaScript code connections to the model context protocol (MCP) server, allowing remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected systems.
Two Cisco Secure Firewall Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) and Software and Cisco Secure Firewall Threat Defense (FTD) VPN Web server Software vulnerabilities (CVE-2025-20333, CVE-2025-20362) were identified in October, which allows authenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code on an affected device caused due to improper validation of input in HTTP requests.
WordPress plugins recorded a larger number of exploitable vulnerabilities, accounting for nearly 326 of vulnerabilities published in October alone, way more than in September. Of those 26 (~ 8%) are deemed critical, with about 8 having a high degree of exploitability of greater than 50% likelihood in the coming months. CVE-2025-7526 and CVE-2025-7634 were caused by WP Travel Engine plugin, used by over 20,000 WordPress sites in the travel sector, caused by arbitrary file deletion vulnerability caused by insufficient file path and allowing unauthenticated attackers to perform local file inclusion respectively. WooCommerce Designer Plugin CVE-2025-6439 allows unauthenticated users to delete any files on the server, potentially causing RCE or data losses. A handful of WordPress CVE-2025-7721, CVE-2025-9485, CVE-2025-10294, CVE-2025-9209, CVE-2025-6388 relate to various WordPress plugins and themes reported causing issues like privilege escalation, authentication bypass, and arbitrary file upload leading to remote code execution. In general, it appeared like attacks favoring unauthenticated file deletions or inclusion type attacks, and targeting RCE compromise without requiring prior logins.
Microsoft accounted for about 52 published known vulnerabilities in the month. Of which, 3 were reported to be high scores and had high exploitability including CVE-2025-24990, CVE-2025-59237, CVE-2025-59501. A critical privilege elevation flaw in the Windows Agere Modem Driver (CVE-2025-24990) present in supported Windows versions up to Server 2025 flaw resulting from legacy driver code removed rather than patched. This vulnerability allows attackers to gain local admin access even if the modem hardware is inactive, making it a widespread and serious threat. Two other critical vulnerabilities such as CVE-2025-59237 and CVE-2025-59501 broadly fit the pattern of RCE and privilege escalation in Windows services and components, emphasizing the critical need for immediate patch installation. CVE-2025-59237 is significant with about 69% EPSS percentile, and potentially active exploits available, demonstrating high risk for enterprise environments. A potential Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) flaw is known to execute arbitrary code remotely by exploiting weaknesses in Edge’s security controls. CVE-2025-60711 is a protection mechanism failure vulnerability that seems to have prevented unauthorized code execution from being bypassed or failing to work properly.
On the advisory side, Microsoft’s October 2025 Patch Tuesday reported nearly 175-193 vulnerabilities, including 7-9 critical and over 150 important flaws across Windows, Office, Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), graphics components, device drivers, and Microsoft Edge. Fixes for 6 zero-day vulnerabilities, of which 4 are exploited in the wild. Exploitation trends primarily targeted RCE (about 30), privilege elevation (about 80), and information disclosures (about 28).
Top Weaknesses
US ProTech identified several top weaknesses (CWE) that contributed to critical vulnerabilities during the month. Of the 408 critical vulnerabilities correlated in October alone, 89 (~ 22%) were CWE-74 Improper Neutralization injection weakness types, followed by 76 (~ 18%) CWE-119 Improper Restriction of Operations or buffer overflow, and 28 (~ 7%) CWE-89 SQL Injection weakness types. The trend seems to have a higher bias towards buffer overflow pattern of attacks during the month when compared to September.
Recent Critical Vulnerabilities – Fall 2025
US ProTech suggests that you pay attention to these top critical vulnerabilities that are likely exploitable this month.
Living in times of change does not mean life changes to the time at hand.
Hold Your Ground!
If you want more info about how CDM-SIEM has impacted Host-Based IT Systems and Air Gapped OT Systems,
Anamo’s patented technology has you covered!
The Anamo Agent is a Host-Based CDM-SIEM which autonomously interrogates a wide variety of systems internally. The reason that this is important is because all other SIEM products and services are external to the Host and network-based which leaves then “Blind” to essential forensics and the ability stop “Unauthorized Privileges Account Escalation” which is proven to be the #1 Data exfiltration Cybersecurity risk.
Below: An “always-on” Risk Assessments of every System, Software, User, Group, Port, Permission, Transaction, and more…. Conducted continuously, without data entry, scheduling, or activation. Imagine that…. the work is done for you and the Platform never sleeps, takes brakes, get sick or runs off on vacation. Now you can get the facts, see the results of CDM, and find time to do what every IT executive must do…. The other 1,000 tasks which await us all!
Contact US ProTech about Anamo today to get your own extended free trial.
The fact is… the smartest organizations have already taken the step towards gaining a real understanding of Risk and Behavioral analytics with Anamo’s patented technology and its ability to correlate data that’s never been harnessed before, until today!